More information
Main author
Espanet, B.
Co-Authors
Minicucci, E.; Depriester, J.-P.
Type of media
Publication type
Lecture
Publication year
-
Publisher
17. EVU Conference, Nice
Citation
Espanet, B.; Minicucci, E.; Depriester, J.-P.: Matter and Morphological Analysis of Forensic Marks in Road Accident Analysis. 17th EVU Conference, Nice 2008
English, 14 pages, 26 figures, 11 references
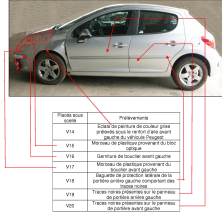
The Vehicle forensic Department of the Institute for Criminal Research of the French Gendarmerie Nationale (Institut de recherche criminelle de la gendarmerie nationale – IRCGN) comprises three expertise units named: Mechanical Identification, Chemical identification and Accidentology. The latter is mainly in charge of the vehicle identification during a criminal case and the accident analysis during civil cases. When analysing road accidents, it is useful and sometimes necessary to read into the potential forensic traces, in order to built accident scenarios hypothesis. The IRCGN vehicle service is specialised in the analysis of such traces which are the reminisence of the vehicle interaction with its environment and its driver. To illustrate this approach, automotive paint systems and their caracteristics will be presented. Different polymers analysis techniques will be exposed: Optical microscopy, pyrolysis, gas chromatography, spectrometry,infra red and Raman spectroscopy.... These techniques can identify nearly all automotive polymers, including paints. Other traces analysis examples will be presented: clothes, tyres.... Matter transfer (simple or crossed) will be treated as well because through them vehicle types (even vehicle itself) can be identified and links can be established between the three different components (Human, Vehicle and Environment) of a Road Accident.
When dedicated to the criminal forensic traces potential, these approaches are pertinent to establish road accident scenarii and then reconstruct the occurence. When dedicated to the criminal forensic traces potential, these approaches are pertinent to establish road accident scenarii and then reconstruct the occurence.
Analyse morphologique et matière des traces lors d’un accident de la route
Français, 16 pages, 26 figures, 11 références
Le département criminalistique Véhicules de l’Institut de recherche criminelle de la gendarmerie nationale (IRCGN) française comporte trois unités d’expertise intitulées : unité d’expertise Identification
Mécanique, unité d’expertise Identification Chimique et unité d’expertise Accidentologie. Ce département a reçu deux principales missions criminalistiques qui sont l’identification de véhicules impliqués dans la commission d’une infraction au code pénal et l’analyse d’accident routier dans des cas judiciaires.
Dans le cas de l’analyse d’accident routier, il est très utile, voire nécessaire, d’exploiter le potentiel d’indice(s) des traces criminalistiques, de façon à construire des hypothèses en termes de séquences d’accident. Le département Véhicules de l’IRCGN s’est spécialisé dans l’exploitation desdites traces qui sont les vestiges de l’interaction du véhicule avec son environnement, avec son conducteur.... Pour illustrer cette approche, sont notamment présentés les systèmes de peintures automobiles et leurs caractéristiques. Différentes techniques d’analyse de polymères sont exposées : la microscopie optique, la pyrolyse / chromatographie en phase gazeuse / spectrométrie de masse, la spectroscopie infrarouge, la spectroscopie Raman.... Ces techniques permettent de discriminer la plupart des polymères automobiles dont les peintures. D’autres exemples d’analyse concernant d’autres types de traces sont abordés: vêtement, traces de pneumatiques.... Les notions de transferts de matière, simples et croisés, sont mises en exergue car elles permettent d’identifier un type de véhicule, voire d’identifier un véhicule, d’établir des liens criminalistiques entre les différents composants Humain(s), Véhicule(s) et Environnement(s) impliqués dans la production d’un accident routier.
Dédiées à l’exploitation du potentiel d’indice(s) des traces criminalistiques, ces approches sont particulièrement pertinentes pour poser les séquences d’un accident routier, puis pour le reconstruire.